How to Choose the Right Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor for Your Engine
Brian Craig
May 10, 2023
Exhaust gas temperature (EGT) sensors are crucial components in modern engines, particularly those with forced induction systems. Exhaust gas temperature sensors are provide real-time temperature readings of the exhaust gases that are used by the engine control unit to regulate fuel injection and ignition timing.
By monitoring exhaust gas temperature, the engine control unit (ECU) can optimize engine performance, reduce emissions, and prevent damage to the engine caused by overheating. This blog post will provide a comprehensive guide on how to choose the right exhaust gas temperature sensor for your engine. It will cover the different types of EGT sensors available, how they work, factors to consider when choosing one, key features to look for, installation and maintenance tips, and common problems that may arise.
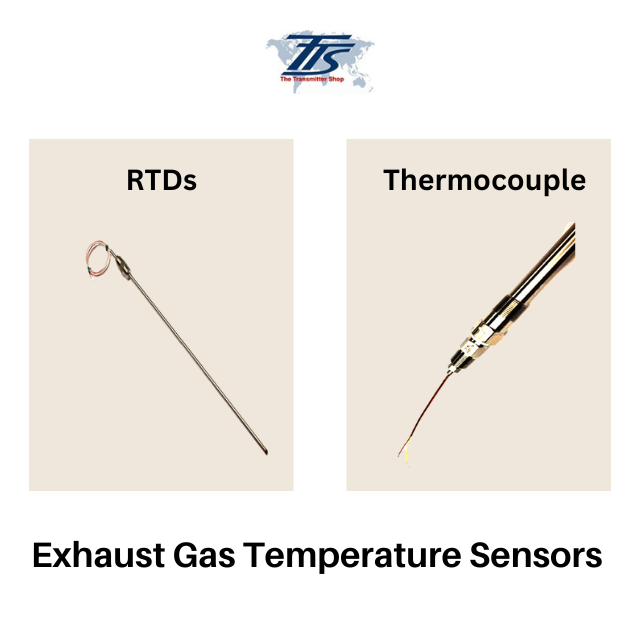
What is an Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT) Sensor?
An Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT) sensor is an electronic device that measures the temperature of the exhaust gases in a combustion engine. The sensor is typically installed in the exhaust system and is used to monitor the temperature of the exhaust gases in real-time. These sensors helps to optimize the fuel-air mixture and ensure the efficient operation of the engine. It is also used to monitor the performance of emission control systems and to prevent damage to the engine caused by excessive heat. The sensor can be of various types, including thermocouples and resistance temperature detectors.
How an Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Works?
Exhaust gas temperature sensor works with temperature-sensing elements such as thermocouples, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), infrared sensors and gas temperature probes that are installed in the exhaust system. The sensor measures the temperature of the exhaust gases and converts it into an electrical signal that sent to the engine control unit.
The engine control unit uses the data to optimize the engine's fuel-air mixture, adjust the engine's performance, and prevent damage to the engine caused by excessive heat. The type of sensing element used depends on the specific application, and each type has its benefits and limitations.
Types of Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensors
There are different types of exhaust gas temperature sensors available in the market with its unique advantages and limitations. Here we will discuss the different types of exhaust gas temperature sensors and their characteristics.
- Thermocouple: Thermocouple is a type of exhaust gas temperature sensor that works based on the principle of Seebeck effect. It consists of two different types of metal wires joined at one end, forming a junction. When the junction is exposed to a temperature difference a voltage is generated, which can be measured to determine the temperature. Thermocouples are widely used in exhaust gas temperature measurements due to their wide temperature range, high accuracy, and fast response time.
- Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD): Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) is another type of exhaust gas temperature sensor that works based on the principle of the resistance change of metal wires with temperature. An RTD is typically made of a metal wire, such as platinum or nickel, whose resistance increases with temperature. The change in resistance is then measured to determine the temperature. RTDs are known for their high accuracy, stability, and repeatability, making them suitable for precise temperature measurements in exhaust gas applications. However, they are generally slower in response time compared to thermocouples.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor
- Type of engine: The type of engine you have will determine the type of EGT sensor you need. For example, diesel engines typically require thermocouple sensors due to their high exhaust gas temperatures, while gasoline engines may use either thermocouple or RTD sensors.
- Type of fuel used: The type of fuel you use can also affect the choice of EGT sensor. Different fuels produce different exhaust gas temperatures, and sensors need to be calibrated to provide accurate readings for each type of fuel.
- Operating conditions: The operating conditions of your engine, such as its load and RPM range, can also affect the choice of EGT sensor. For high-performance engines that operate at high RPMs, fast-response thermocouple sensors may be needed to provide accurate temperature readings.
- Budget:The cost of EGT sensors can vary widely depending on their features and quality. It's important to choose a sensor that provides the necessary accuracy and durability for your engine, while staying within your budget.
Features To Look For In an Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor
- Durability: EGT sensors are exposed to high temperatures and harsh environments, so it's important to choose one that is built to last. Look for sensors made from high-quality materials and with a proven track record of reliability.
- Accuracy: Accuracy is crucial when it comes to EGT sensors, as even small variations in temperature readings can have a big impact on engine performance. Look for sensors that provide precise and consistent temperature readings.
- Response time: The response time of an EGT sensor is the time it takes for the sensor to detect and report a change in temperature. Fast-response sensors are essential for high-performance engines that require precise temperature control.
- Compatibility: Make sure that the EGT sensor you choose is compatible with your engine and ECU. Some sensors may require.
Why Is Exhaust Gas Temperature Monitoring Important?
The exhaust gas temperature gauge provides vital information about engine load, combustion quality, and potential thermal stress. Overheating can cause engine knock, turbocharger failure, and damage to exhaust system components.
Key Benefits of Monitoring EGT:
1. Boosts Fuel Efficiency: By analyzing EGT data, engines can be tuned for more complete combustion, reducing fuel waste. This leads to better mileage and lower operating costs.
Header Variations:
• Improves Fuel Economy
• Enhances Engine Efficiency
• Optimizes Fuel Consumption
2. Prevents Engine Overheating: High exhaust temperatures indicate thermal stress, which can harm pistons, valves, and turbochargers. Monitoring helps avoid engine knock and costly damage.
Header Variations:
• Avoids Overheating Risks
• Protects Against Thermal Damage
• Maintains Safe Operating Temperatures
3. Reduces Emissions: EGT monitoring enables better control of combustion and after-treatment systems, lowering harmful emissions like NOx. It ensures compliance with emission regulations.
Header Variations:
• Controls NOx and Pollutants
• Supports Emission Compliance
• Helps Cut Exhaust Emissions
4. Extends Component Lifespan: Stable exhaust temperatures reduce strain on key components like diesel particulate filters (DPFs) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems. This results in fewer replacements and lower maintenance costs.
EGT Sensor Life and Failure Causes
In industrial applications like Oil & Gas, Chemical, or Food Processing plants, EGT sensors typically last several years but are highly dependent on environmental conditions and process intensity. Frequent exposure to high temperatures, corrosive elements, and continuous operation can accelerate wear and reduce sensor life.
Common Causes of EGT Sensor Failure in Industrial Settings:
1. Thermal Cycling Fatigue: Processes with repeated start-stop cycles, like in pharmaceutical reactors or batch food processing, cause frequent heating and cooling. This thermal stress gradually weakens sensor materials and leads to micro-cracking and failure.
2. Exposure to Contaminants: In refineries and chemical plants, exposure to oil mist, carbon soot, cleaning agents, or volatile compounds can degrade sensor tips. These deposits impair thermal conductivity and skew temperature readings, reducing process control accuracy.
3. Moisture Ingress or Corrosion: EGT sensors installed in humid or washdown environments—common in food & beverage or wastewater treatment—are prone to moisture intrusion. Internal corrosion leads to erratic readings or sensor failure, particularly in poorly sealed systems.
4. Wiring Damage from Heat or Vibration: High-vibration equipment in Oil & Gas or wastewater pumping stations can strain and eventually fracture wiring. Prolonged heat exposure from nearby process lines can also degrade insulation, leading to signal loss or short circuits.
5. Sensor Tip Erosion from High-Velocity Gas Flow: In flue gas systems or high-flow exhaust stacks—especially in refining or chemical combustion units—gas velocity can erode the sensor tip over time. This degrades sensor sensitivity and shortens service life in critical monitoring points.
6. Harsh Environmental Exposure: Industries like petroleum refining and chemical processing expose sensors to corrosive gases, abrasive particulates, and extreme heat. These harsh conditions significantly reduce sensor longevity and demand regular inspection and replacement.
Exhaust Gas Temperature sensors play a crucial role in optimizing engine performance, reducing emissions, and preventing damage to the engine caused by overheating. By choosing the right EGT sensor and properly installing and maintaining it, you can ensure the efficient and safe operation of your engine. The Transmitter Shop (TTS) is a distributor of superior quality remanufactured thermocouple, RTDs, Thermometer, Transmitters and Thermowells originally sourced from reputed brands such as Rosemount, Foxboro, Thermo-Probes and so on. The company specializes in remanufacturing, reconditioning, and calibration of devices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
What does an exhaust temperature sensor do?
An exhaust temperature sensor measures the temperature of gases leaving the engine or industrial burner. It helps optimize combustion, control emissions, and protect components from overheating.
How do you measure the temperature of exhaust gas?
Exhaust gas temperature is typically measured using thermocouples inserted into the exhaust stream. These sensors convert heat into electrical voltage, which is interpreted by a control unit.
What is the purpose of the exhaust gas temperature gauge?
The exhaust gas temperature gauge displays the real-time temperature of exhaust gases. It helps operators monitor engine or process health and prevent thermal overload.
What is the instrument for exhaust gas temperature?
The primary instrument is an exhaust gas temperature sensor—usually a thermocouple—paired with an ECU or gauge to interpret the readings.
What device uses a thermocouple to measure exhaust temperature?
EGT sensors use thermocouples (like type K or type J) to measure and transmit exhaust temperature data.
Related Posts
- Important Calibration Tips for Pressure Sensors
- What is RTD Sensor and How Does it Work?
- What is a Thermocouple and How Does It Work?
- Why Platinum is a Preferred Choice in RTD Sensors?
- How to Choose the Right Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor for Your Engine
- Role of Sensors in the Food Processing Plant
- How Can Greenhouse Gas Emissions Be Reduced?
- Understanding Electrochemical Detection: Principles, Techniques and Environmental Application
- Furnace Flame Sensor Faults: Everything You Need to Know for Safe Operation
- Complete Hydrogen Gas Safety and Measurement Solutions
- Key Sensors for Monitoring Emissions in Wet and Dry Scrubber Systems
- What is a Mass Flow Meter? Working Principles and Key Benefits
- Electromagnetic Flow Sensors for Abrasive and Corrosive Fluids
- Pressure Sensing Sensor Modes of Measurement: Key Differences and Benefits
- Flow Measurement Challenges in Subsea Operations
- Pressure Sensing Sensor Modes of Measurement Key Differences and Benefits
- Electromagnetic Flow Sensors for Abrasive and Corrosive Fluids
- Mass Flow Meters and Their Working Principles
- Best Explosion Proof Switches for Hazardous Environments
- Best Explosion Proof Switches for Hazardous Environments
- Furnace Flame Sensor Faults Everything You Need to Know for Safe Operation
- Pneumatic Pressure Controllers: A Safe Choice for Hazardous Areas
- A Practical Guide to Vacuum Measurement and Operation
- Understanding Electrochemical Detection: Principles, Techniques and Environmental Application
QUICK ENQUIRY







